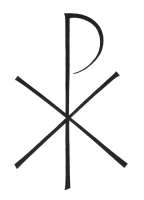
An Overview of Christian
History
compiled by Felix Just, S.J., Ph.D.
Highlights from and Supplements to
People of God: The History of Catholic Christianity
by Anthony E. Gilles (St. Anthony Messenger Press, 2000)
Jump to Chapter 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | Typos | Summary
The Main Stages of Christian History:
Gilles' Preface:
Ch. 1 - Introducing the Early Church (AD 90's - 380's)
Ch. 2 - The Early Church Defines Orthodox Christianity (AD 313 - 451)
Ch. 3 - The Fall of Rome and the Rise of the Western Church (AD 370's - 604)
Ch. 4 - Concluding the Age of the Church Fathers (AD 95 - 636)
Ch. 5 - Papacy and Empire Vie for Control of the Church (ca. AD 600 - 1150)
Ch. 6 - Catholics, Byzantines, and Muslims (AD 483 - 1054)
| Feature: | Western / Roman / Catholic | Eastern / Byzantine / Orthodox | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dominant Language: | Latin |
Greek |
||
| Religious Center: | Rome (Central Italy) | Constantinople | ||
| Imperial Capital (by 800's): | Aachen (Northern Germany) | Constantinople | ||
| Church Authority: | Pope is the leader of all other bishops | All Patriarchs/Bishops are equal | ||
| Church/State Relations: | Church seeks to be independent | Church influenced/controlled by State | ||
| Political Reality: | Lots of small kingdoms, mostly separate; "Holy Roman Emperor" rarely strong |
One unified (but shrinking) Empire; "Byzantine Emperor" sole leader |
||
| Muslim Influence: | Little fear of invasion in Europe after 732; Muslims control only Spain (less & less) |
Muslims often threaten Eastern borders; conquer more and more over time |
||
| Celebration of Eucharist: | Daily "Mass" | Weekly "Divine Liturgy" | ||
| Communion Bread: | Unleavened | Leavened | ||
| Clerical Celibacy: | Required | Optional (mostly for Monks) | ||
| Sacrament of Confirmation: | Separate from Baptism; Administered only by bishops |
Together with Baptism; Administered by any priests |
||
| Holy Spirit "proceeds" from | "the Father and the Son" (filioque; added) | "...the Father" (only; as in Creed of 381) | ||
| Sign of the Cross: | four fingers; top/bottom/left/right | three fingers; top/bottom/right/left | ||
| Religious Art: | some use of paintings & statues | elaborate use of icons, mosaics, etc. | ||
| Cultural Emphasis: | law, order, practical matters | theology, aesthetics, intellectual ideas | ||
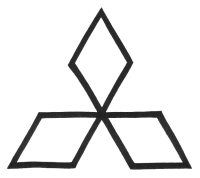
Common Cross Shapes: |
 |
 |
 |
|
Ch. 7 - The Vanishing Dream of Catholic Christendom (AD 1095 - 1377)
Ch. 8 - The Church's Intellectual Life (AD 735 - 1415)
Ch. 9 - Everyday Life in the Catholic Middle Ages (ca. AD 1150 - 1350)
Ch. 10 - The End of Catholic Middle Ages (ca. AD 1300 - 1500)
Ch. 11 - Entering the Age of Reformation (AD 1450's - 1520's)
Ch. 12 - The Reformation: Protestant Phase One (AD 1517 - 1555)
| Martin Luther's Life | The Catholic Church |
|---|---|
| 1483, Nov. 10 - born in Eisleben, Germany | . |
| 1503 - enters Augustinian Order; scrupulous religiosity | 1503-13 - Pope Julius II (begins building St. Peter's Basilica) |
| 1507 - ordained a priest; | . |
| 1510 - visits Rome; shocked by Church's wealth & corruption | 1513-21 - Pope Leo X (member of rich & powerful Medici family) |
| 1517, Oct 31 - posts "95 Theses" on door of castle church in Wittenberg; attacks sale of indulgences and other abuses of Pope & Church | 1516 - Johann Tetzel, OP, promotes indulgences all over Germany to help finance continuing construction of St. Peter's; later writes against Luther |
| 1518 - hearing in Augsburg; refuses to recant his writings or teachings | 1519 - Charles V crowned Holy Roman Emperor |
| 1520 - writes "To the Christian Nobility of the German Nation"; "On the Babylonian Captivity of the Church"; & "On the Freedom of a Christian" 1520, Dec. 12 - publicly burns the papal bull, Exsurge Domine |
1520, June 15 - Pope Leo X writes Exsurge Domine, a "bull"
threatening Luther's excommunication; 1521, Jan. 3 - a second papal "bull" excommunicates Luther |
| 1521, April 17 - civil trial at Diet of Worms; banned from H.R. Empire | . |
| 1522 - retreats to Wartburg Castle; translates Bible into German | 1522-23 - Pope Adrian VI (attempts reforms, but soon dies) |
| 1524 - opposes peasant revolt; tells princes to crush the "mad dogs" | 1523-34 - Pope Clement VII (another Medici) |
| 1525 - marries ex-nun, Katharina von Bora; fathers four children | . |
| 1529 - Luther publishes Large Catechism & Small Catechism | . |
| 1530 - "Augsburg Confession" written by Luther's associate Melancthon | 1534-49 - Pope Paul III (begins serious reforms; calls Council of Trent) |
| 1546, Feb. 18 - dies while visiting family in Eisleben, his hometown | 1545-63 - Council of Trent |
| [1555 - Peace of Augsburg - "cuis regio, eius religio"] | 1555-59 - Pope Paul IV (super-strict reformer) |
Ch. 13 - The Reformation: Protestant Phase Two (AD 1520's - 1620's)
The Protestant Reformation spreads quickly throughout Central and Northern Europe (see the handout maps!), but splintered into many different factions or denominations, already during Luther's lifetime. The following were the earliest and/or largest groups:
Ch. 14 - The Reformation: The Catholic Phase (AD 1500's)
Ch. 15 - The Reformation: Its Bleak Aftermath (AD 1600's - 1700's)
Ch. 16 - The Church in the New World (AD 1492 - 1960)
 Catholicism and Anti-Catholicism in America:
Catholicism and Anti-Catholicism in America:
Ch. 17 - The Church Reacts to the Modern World (AD 1770's - 1900's)
Ch. 18 - The Path of Protestantism (AD 1550's - 1880's)
Ch. 19 - The Age of Vatican II (AD 1890's - 1960's)
Ch. 20 - The Post-Vatican II Church (AD 1960's - today)
Ch. 21 - Visions and Boundaries (AD 1960's - today)
Typographical Errors in People of God:
| Error: | Correction: | |
|---|---|---|
| presbuteros or priest | presbuteros or elder | |
| Benedict's, sister | Benedict's sister (w/o comma) | |
| Augustine, Athanasius, Jerome | [Athanasius was Eastern, not Western; correct on p. 79] | |
| See the map on page 49... | [map does not show Aquitaine, Burgundy, Austrasia, etc.] | |
| wondering poets | wandering poets | |
| Ignatius Loyola (1495-1556) | (1491-1556) | |
| Within twenty-five years of their founding | Within sixteen years... (by the time Ignatius died, 1556) | |
| Pierce named William Campbell the first... | Pierce named James Campbell the first | |
| 1534 Ignatius Loyola founds... | 1540 Ignatius Loyola founds... | |
| 1648 Thirty Year's War | 1648 Thirty Year's War ends (began 1618) | |
| Error: | Correction: | |
| Valentinian (364-375) | Valentinian I (364-375) - also Valentinian II (375-392) | |
| 350: Arian Constantine II | 350: Arian Constantius II | |
| 612: Muhammad establishes religion of Islam | 622: Muhammad establishes religion of Islam | |
| Teresa of Avila (182?) | Teresa of Avila (1582) | |
| 1431: Council of Basle | 1431: Council of Basel | |
| 1506: John Tetzel sells indulgences | 1503 (or 1516): John Tetzel... | |
| Francis II (France; 1559-1560) | [listed twice] | |
| 1534: Society of Jesus founded... | 1540: Society of Jesus founded... (correct on p. 136) | |
| 1577: Book of Concord prepared... | 1580: Book of Concord prepared... |
The Key Ecumenical Councils: (see Prof. Just's Ecumenical Councils webpage for their details & documents of each Council)
| Date: | 325 | 381 | 431 | 451 | 1215 | 1414-17 | 1545-63 | 1869-70 | 1962-65 |
| Place: | Nicea | Constantinople | Ephesus | Chalcedon | Lateran IV | Constance | Trent | Vatican I | Vatican II |
Other Key Dates, People, and Developments in the History of Christianity: (in addition to the Ecumenical Councils listed above)
(see also Gilles, Focus 40, pp. 197-98)
[Note:
The dates, people, and events in the following three columns do NOT exactly line up with the information in the same lines of the other two columns;
but each of the three columns is itself in chronological order.]
| Other Key Dates: | Key People: | Key Developments: |
|
[Note: 4 BC |
Mary & Joseph of Nazareth Jesus of Nazareth / Jesus Christ The Apostles, esp. Peter & Paul Emperors Nero, Decius, Diocletian Emperor Constantine Athanasius of Alexandria Jerome Pope Leo the Great Bishop Augustine of Hippo Benedict of Nursia {Prophet Mohammed} Emperor Charlemagne Pope Gregory VII Pope Innocent III Bernard of Clairvaux Francis of Assisi Dominic Guzman Thomas Aquinas Catherine of Siena Martin Luther John Calvin King Henry VIII Ignatius of Loyola Teresa of Avila John Wesley John Carroll Pope Pius IX Isaac Hecker Elizabeth Ann Seton Pope Pius XII Popes John XXIII & Paul VI Mother Teresa of Calcutta Pope John Paul II Pope Benedict XVI |
Birth of Jesus Life, Crucifixion, Death, and Resurrection of Jesus Gradual Separation of Christianity from Judaism Persecutions of Christians by Rome Constantine's Conversion & Edict of Milan Early Christian Heresies, Councils, & Creeds Rise of Papal Primacy Fall of the Western Roman Empire Growth of Monasticism (hermits, Benedictines) Rise of Islam & Muslim Conquests Iconoclast Crisis Carolingian Renaissance Great Schism (Eastern Orthodox vs. Western Catholic) Lay Investiture Controversy Gregorian Reform Crusades (esp. First through Fourth) Mendicant Religious Orders (Franciscans & Dominicans) Scholasticism & Medieval Universities Avignon Papacy (Babylonian Captivity of the Popes) Western Schism (multiple rival Popes) Late Medieval Crises (100 Years' War, Black Plague) Renaissance & Humanism Gutenberg's Moveable-type Printing Press Protestant Reformation (Lutheran, Reformed, Radical branches) Separation of the Church of England (Anglicanism) Counter-Reformation (Jesuits & Council of Trent) Religious Wars/Persecutions in Europe Colonial Expansions in the Americas (N & S) Religious Freedom, Diversity, Tolerance/Intolerance in N. America French Revolution & Its Aftermath (Liberalism, Democracy) Modernism & Anti-modernist Reactions Catholicism & Anti-Catholicism in USA (before & after 1776) Papal Encyclicals & Reform Movements before Vatican II Second Vatican Council (final documents & implementation) |
Some Broader Synthesizing Questions:
GLOSSARY: For definitions of many of the following terms, see the glossaries and indices in the back of our textbooks: Gilles (pp. 229-34, 235-51) or Rausch (pp. 246-61, 273-82). For other terms, check a good published dictionary, or online resources like dictionary.com, or see the Biblical Glossary on Prof. Just's website.
Some Early Christian "Heresies": Adoptionism, Arianism, Docetism, Donatism, Gnosticism, Marcionism, Modalism, Monarchianism, Monophysitism, Nestorianism, Pelagianism, Subordinationism
Some Later Christian Groups and Denominations: Albigensians, Anabaptists, Anglicans, Baptists, Calvinists, Catholics (Roman), Episcopalians, Jansenists, Lutherans, Methodists, Orthodox (Eastern, Greek, Russian, etc.), Presbyterians, Puritans, Reformed Christians, etc.
Some Major Religious Orders within Catholicism (and their founders): Benedictines (St. Benedict of Nursia), Cistercians (St. Bernard of Clairvaux), Dominicans (St. Dominic Guzman), Franciscans (St. Francis of Assisi), Jesuits (St. Ignatius of Loyola), Paulists (Isaac Hecker), Sisters of Charity (St. Elizabeth Ann Seton), etc.
Subfields of Theology: biblical theology, christology, ecclesiology, ecumenism (ecumenical dialogue), eschatology, feminist theology, inter-religious relations (interfaith dialogue), liberation theology, liturgy, missiology, moral theology/ethics, pneumatology, soteriology, social ethics, spirituality, systematic theology, trinitarian theology, etc.
Some Biblical Terms: apostle, Bible, canon, covenant, evangelist, Gospel, Hebrew Bible, noncanonical books, New Testament, Old Testament, Septuagint, Synoptic Gospels, Torah, Vulgate (see also Prof. Just's "Biblical Glossary")
Other Important Terms used in Gilles:
anti-Catholicism, apology, apostate, apostle/apostolic, ascetic/asceticism, Assumption (of Mary), baptism, barbarian, basilica, bishop/episcopal, bishops' conferences, Byzantium/Byzantine, cardinals, Carolingian Reform, catechesis/catechumen, cathedral, Catholic/catholic/catholicity, celibacy, Christ/Messiah, Christendom, Church/church (4 meanings), clergy & laity, Concordat, contemplation (prayer), conversion, council/conciliarism, creed/creedal formulas, crusades, curia, deacon/diaconal, Desert Fathers, diocese/diocesan, Doctor of the Church, doctrine/doctrinal, dogma/dogmatic, dualism, ekklesia/ecclesial, Ecumenical Councils, encyclical (papal), episkopos/episcopal/Episcopal, Eucharist, evangelical, Evangelist/evangelist, evangelize/evangelization, excommunication, feudalism (lords & vassals), filioque, friars/mendicants, fundamentalist, Gospel/gospel, grace, heaven/hell, heresy/heterodox, hierarchy, Holy Spirit, homoousios, hypostasis & hypostatic union, icons/iconoclasm, Immaculate Conception, imprimatur, incarnation, indulgences, infallibility, Inquisition/inquisitor, inspiration, justification (by faith), kerygma, lay investiture, lectio divina, liturgy, local church, logos, martyrs/confessors, Mass, meditation, modernist crisis, monastery/monasticism, monks/hermits, nationalism, nepotism, ontological, Orthodox/orthodox, pagan, papacy/papal, parish, patriarch, patristic fathers/writings, penance, piety/pious devotions, pontiff, Pope, predestination, presbyter/elder, priest, primacy (papal), purgatory, real presence, reconciliation, reform/reformation, relics, religious (brothers/sisters/orders), Renaissance, revelation/Revelation, Roman Curia, rule of faith, Sabbath, sacrament, saint/sanctity, salvation, schism, Scholasticism, secular, simony, (four) solas of Protestantism, Syllabus of Errors, synagogue, synod, theocracy, Theotokos, Thomism, traditions/Tradition, transubstantiation, Tridentine, T.U.L.I.P., "works of the Law" vs. "good works"
Jump to Gilles' Chapter 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | Typos | Summary
Return to the Homepage of Prof. Felix Just, S.J.